Difference between revisions of "8.3 Determining the viability of Design Solutions"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "==8.3a Assess design solutions viability== #The design solutions impact on user lifestyles: Designers aim to prove the viability of new products and show that they will have a...") |
m |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
##there is strong competition for the materials or parts. | ##there is strong competition for the materials or parts. | ||
##the materials have an impact on sustainability. | ##the materials have an impact on sustainability. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Sustainability== | ||
| + | #Products can be designed so that parts which commonly fail can be easily replaced. Such parts might include batteries or touchscreens. | ||
| + | #The use of standard parts helps achieve this, as does making the spare parts readily available on the open market. | ||
| + | #Providing a service/maintenance schedule so that the product is regularly maintained and kept working to a high standard. | ||
| + | #Servicing can spot problems early on and correct these cheaply before the problem develops into a full product failure | ||
| + | #Providing freely available service manuals so that independent repairers can tackle the problem and not just franchised dealers. | ||
| + | #Designing the product so that standard tools and diagnostic equipment can be used to trace faults and fix them. | ||
| + | #Using higher quality components which are less likely to failure prematurely, and designing the product so that the components are working well within their rating and not being stressed. | ||
| + | #Offering products on a leasing basis where the product continues to be owned by the manufacturer therefore there is an interest to design the product differently. | ||
| + | #Providing facility for regular software updates to fix known issues and to keep the product in line with the features available on the latest models. The same applies to hardware updates, e.g. new cases, better cameras etc. | ||
| + | #By adopting economic models for profit based on usage rather than one-off sale, manufacturers will focus their efforts on customers keeping and using the product, rather than replacing it, e.g. monthly subscription charges which include servicing and upgrades. | ||
==Costs and profit== | ==Costs and profit== | ||
Revision as of 10:35, 19 April 2023
Contents
- 1 8.3a Assess design solutions viability
- 2 How well the product performs
- 3 Technical difficulty of manufacture
- 4 Stock availability of materials and components
- 5 Sustainability
- 6 Costs and profit
- 7 Timescales involved
- 8 Promotion, brand awareness and advertising potential
- 9 Balancing supply and demand
- 10 Market analysis of similar products
8.3a Assess design solutions viability
- The design solutions impact on user lifestyles: Designers aim to prove the viability of new products and show that they will have a positive impact on user lifestyles.
- For example, mobile phones have had a large impact on user lifestyles as they have become lighter and able to complete more computational tasks.
- These solutions could also have negative impacts on user lifestyles, using the mobile phone example again, fewer people are communicating face-to-face and getting out.
How well the product performs
- Feasibility studies confirming that a product will meet performance standards are vital if the product is to be viable.
- Companies want the user to perceive the need for a product and will spend a lot of time and money trying to research user needs and wants through many different forms, such as questionnaires.
Technical difficulty of manufacture
- A major deciding factor in the production of a product is the costs associated with the difficulty of its manufacture.
- Designers and manufacturers aim to reduce the costs of manufacturing by adapting and simplifying products to make them easier to produce.
Stock availability of materials and components
- The availability of stock or ease of obtaining materials can have a large impact on the viability of some products.
- Studies will need to take place to ensure materials and components are easily available prior to manufacture. the following problems can occur if this is not done.
- a material is not available in sufficient quantities or availability is unreliable.
- it will cost a significant sum to buy in
- there is a long lead time
- there is strong competition for the materials or parts.
- the materials have an impact on sustainability.
Sustainability
- Products can be designed so that parts which commonly fail can be easily replaced. Such parts might include batteries or touchscreens.
- The use of standard parts helps achieve this, as does making the spare parts readily available on the open market.
- Providing a service/maintenance schedule so that the product is regularly maintained and kept working to a high standard.
- Servicing can spot problems early on and correct these cheaply before the problem develops into a full product failure
- Providing freely available service manuals so that independent repairers can tackle the problem and not just franchised dealers.
- Designing the product so that standard tools and diagnostic equipment can be used to trace faults and fix them.
- Using higher quality components which are less likely to failure prematurely, and designing the product so that the components are working well within their rating and not being stressed.
- Offering products on a leasing basis where the product continues to be owned by the manufacturer therefore there is an interest to design the product differently.
- Providing facility for regular software updates to fix known issues and to keep the product in line with the features available on the latest models. The same applies to hardware updates, e.g. new cases, better cameras etc.
- By adopting economic models for profit based on usage rather than one-off sale, manufacturers will focus their efforts on customers keeping and using the product, rather than replacing it, e.g. monthly subscription charges which include servicing and upgrades.
Costs and profit
- The need for companies to generate profit means that feasibility studies to carefully plan cost implications and the ability for a product to make a profit.
- Types of costs to consider are:
- Factory rent/mortgage (fixed)
- Power (mixed cost)
- Insurance (Fixed)
- Wages (Variable costs)
- Miscellaneous expenses (variable costs)
- Machinery (fixed)
- Materials (variable cost)
- Tooling (variable cost)
Timescales involved
- The timescales involved in bringing a product to market are vitally important.
- A product brought too late to the market where a competitor has a large market share can mean real problems in gaining sales and could mean a product and all its related investments will not longer be commercially viable.
- Another timescale must be factored into a feasibility study is obtaining protection of design ideas through intellectual property rights to ensure ideas can not be stolen.
Promotion, brand awareness and advertising potential
- Marketing often dictates the success of a product and its associated commercial viability.
- If consumers are unaware that a product exists, they are unlikely to buy it.
- Companies often use brand awareness and brand identity to cross sell products. As a consumer, you are more likely to buy another product from the same company if you have had a positive experience.
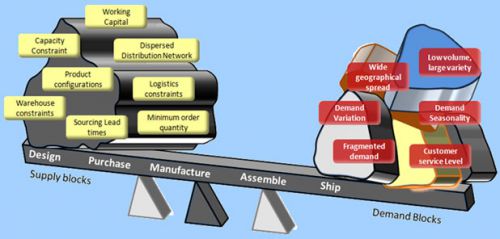
Balancing supply and demand
- Keeping demand and supply in balance is a constant struggle. The consequences of poor customer service, high inventories, cash flow difficulties, and failure to meet planned business goals lead companies in search of a process to better manage the delicate balance of demand and supply.
Market analysis of similar products
- During the product development and after its launch, companies often perform a range of feasibility studies looking at other competitor products, sales trends, marketing promotions and opportunities in new markets.
- During development stages, market analysis is primarily focused on similar products already available to consumers.
- Analysis simply looks at sales trends to show the popularity of a certain product range within a market to determine demand.
- Key terms:
- Brand awareness
- Brand identity
- Electronic point of sale (EPOS)
- Feasibility study.
- Fixed costs.
- Variable costs.