Difference between revisions of "Health and Safety"
(First commit) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<strong>Ensuring Health and Safety when working with materials in a workshop.</strong> | <strong>Ensuring Health and Safety when working with materials in a workshop.</strong> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Health and Safety at work Act 1974== | ||
| + | #An employer's key duties under the act are: | ||
| + | ##Make sure the workplace is safe by carrying out risk assessments. | ||
| + | ##Ensuring machinery and equipment is safe and setting out safe procedures for using them. | ||
| + | ##Ensuring items and substances are stored safely and providing training for using them safely. | ||
| + | ##Providing adequate welfare facilities such as toilets and including first aid arrangements. | ||
| + | ##Promoting employees’ personal health and safety by providing information, training and supervision. | ||
| + | ##Making sure equipment is suitable for the intended use and arranging for annual inspection and maintenance. | ||
| + | ##Providing necessary PPE. | ||
| + | ##Ensuring that mandatory safety signs are provided and maintained. | ||
==9.1a Demonstrate an understanding of safe working practices in the workshop situation, including:== | ==9.1a Demonstrate an understanding of safe working practices in the workshop situation, including:== | ||
| Line 54: | Line 65: | ||
Safety-critical parts of work equipment may need a higher and more frequent level of attention than other aspects, which can be reflected within any maintenance programme. Breakdown maintenance, undertaken only after faults or failures have occurred, will not be suitable where significant risk will arise from the continued use of the work equipment. | Safety-critical parts of work equipment may need a higher and more frequent level of attention than other aspects, which can be reflected within any maintenance programme. Breakdown maintenance, undertaken only after faults or failures have occurred, will not be suitable where significant risk will arise from the continued use of the work equipment. | ||
| − | ==9.2b The responsibility of manufacturers to appropriately label products and offer | + | ==9.2b The responsibility of manufacturers to appropriately label products and offer guarantees to their consumers to deliver the correct levels of product assurance related to safety.== |
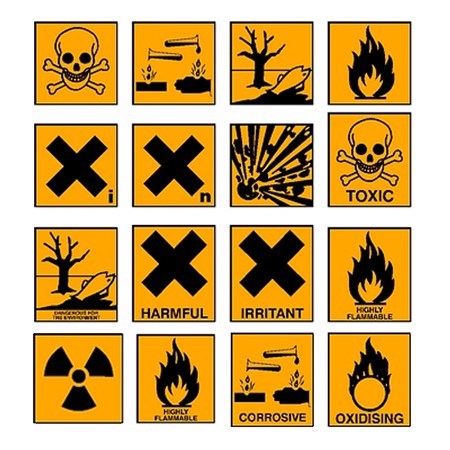
| − | Product | + | Product labelling is covered under the Trade Description Act. Labels must include accurate information to ensure that products can be used safely and correctly. |
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trade_Descriptions_Act_1968 Trade Description Act] | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trade_Descriptions_Act_1968 Trade Description Act] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <strong>Example safety exam question:</strong> | ||
| + | |||
| + | A home lift can be installed in a house where one or more occupants may have mobility problems and may not be able to use stairs easily. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Identify three ways in which the manufacturer of the home lift can ensure the safe operation of the lift by its users | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Provide safety warning labels (e.g. maximum load 2 people) (1). | ||
| + | # Door interlock to prevent lift moving if door is open (1). | ||
| + | # Overweight load sensor (1). | ||
| + | # Key lock to prevent children playing in lift (1). | ||
| + | # Battery backup in case of power failure (1). | ||
| + | # Alarm button to summon help in an emergency (1). | ||
| + | # Also accept design related responses (1) | ||
| + | # Any other valid suggestion | ||
[[Design_Engineering|Design Engineering homepage]] | [[Design_Engineering|Design Engineering homepage]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:44, 1 March 2023
Ensuring Health and Safety when working with materials in a workshop.
Contents
- 1 Health and Safety at work Act 1974
- 2 9.1a Demonstrate an understanding of safe working practices in the workshop situation, including:
- 3 9.1b Demonstrate an understanding of how to work safely with specialist tools, techniques, processes, equipment and machinery during the design and manufacture of products.
- 4 9.2a Demonstrate an understanding of how the regulatory and legislative framework in the health and safety at work act (HASAW) sets out duties of employers and employees in the product manufacturing industries.including:
- 5 9.2b The responsibility of manufacturers to appropriately label products and offer guarantees to their consumers to deliver the correct levels of product assurance related to safety.
Health and Safety at work Act 1974
- An employer's key duties under the act are:
- Make sure the workplace is safe by carrying out risk assessments.
- Ensuring machinery and equipment is safe and setting out safe procedures for using them.
- Ensuring items and substances are stored safely and providing training for using them safely.
- Providing adequate welfare facilities such as toilets and including first aid arrangements.
- Promoting employees’ personal health and safety by providing information, training and supervision.
- Making sure equipment is suitable for the intended use and arranging for annual inspection and maintenance.
- Providing necessary PPE.
- Ensuring that mandatory safety signs are provided and maintained.
9.1a Demonstrate an understanding of safe working practices in the workshop situation, including:
i. understanding the need for risk assessments.
As part of managing the health and safety of your project you must control the risks in your clasrrom environment. To do this you need to think about what might cause harm to you and the people around you and decide whether you are taking reasonable steps to prevent that harm. This is known as risk assessment.
ii. identifying hazards and implementing control measures to minimise risks.
One of the most important aspects of your risk assessment is accurately identifying the potential hazards in the classroom. A good starting point is to walk around your classroom and think about any hazards. In other words, what is it about the activities, processes or substances used that could injure yourself or other students or harm their health?
9.1b Demonstrate an understanding of how to work safely with specialist tools, techniques, processes, equipment and machinery during the design and manufacture of products.
When designing and making your project, you will need to demonstrate you have considered in advance what all the risks are and what you plan to do to minimise the risks.
Once you have considered all the steps and written down what you plan to do, you will then need to do the activity, showing and explaining how you went about implementing all of the H&S strategies.
These can be in the form of photographs or explanations, but you will need to do this for every activity or step.
Implications of health and safety legislation on product manufacture
9.2a Demonstrate an understanding of how the regulatory and legislative framework in the health and safety at work act (HASAW) sets out duties of employers and employees in the product manufacturing industries.including:
i. Control of Substances Hazardous to Health (COSHH).
COSHH stands for 'Control of Substances Hazardous to Health' and under the Control of Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations 2002, employers need to either prevent or reduce their workers' exposure to substances that are hazardous to their health.
Click here to go to the health and safety executive (HSE) website to read more about COSHH.
ii. Personal Protective Equipment at work regulations (PPE).
PPE is equipment that will protect the user against health or safety risks at work. It can include items such as safety helmets, gloves, eye protection, high-visibility clothing, safety footwear and safety harnesses
Click here to go to the HSE website to read more on PPE.
iii. Ensuring machinery is well maintained.
In order to ensure work equipment does not deteriorate to the extent that it may put people at risk, employers, the relevant self-employed and others in control of work equipment are required by PUWER to keep it 'maintained in an efficient state, in efficient order and in good repair'. If the manufacturer is self-employed and their work poses no risk to the health and safety of others, then health and safety law may not apply to them. HSE has guidance to help manufacturers understand if the law applies. Such effective maintenance can not only help in meeting PUWER requirements but can also serve other business objectives, such as improved productivity and reduced environmental impact.
The frequency and nature of maintenance should be determined through risk assessment, taking full account of:
- the manufacturer's recommendations - the intensity of use - operating environment (eg the effect of temperature, corrosion, weathering) - user knowledge and experience - the risk to health and safety from any foreseeable failure or malfunction
Safety-critical parts of work equipment may need a higher and more frequent level of attention than other aspects, which can be reflected within any maintenance programme. Breakdown maintenance, undertaken only after faults or failures have occurred, will not be suitable where significant risk will arise from the continued use of the work equipment.
Product labelling is covered under the Trade Description Act. Labels must include accurate information to ensure that products can be used safely and correctly.
Example safety exam question:
A home lift can be installed in a house where one or more occupants may have mobility problems and may not be able to use stairs easily.
Identify three ways in which the manufacturer of the home lift can ensure the safe operation of the lift by its users
- Provide safety warning labels (e.g. maximum load 2 people) (1).
- Door interlock to prevent lift moving if door is open (1).
- Overweight load sensor (1).
- Key lock to prevent children playing in lift (1).
- Battery backup in case of power failure (1).
- Alarm button to summon help in an emergency (1).
- Also accept design related responses (1)
- Any other valid suggestion